HEALTHY EATING
What is a healthy diet?
A healthy eating includes a balanced and varied diet. Healthy food contains all the necessary nutrients that the body needs to maintain good health. This includes adequate amounts of fruits and vegetables, whole grains, protein, healthy fats, and limited amounts of sugar, salt, and saturated fat.
People often have the misconception that healthy eating is either very boring and one-sided or very expensive. In fact, a healthy diet is definitely not boring, because it includes a varied and colorful menu.
One cannot say that one food is healthy and another is unhealthy. It all depends on how much and how often we consume them. Vegetables should be eaten daily, but pizza less often. If we sometimes eat pizza and ice cream, it does not make us an unhealthy eater and does not make us overweight.
The basis of a healthy diet is a varied menu, with the help of which all the necessary vitamins, minerals and fibers are obtained. It is also important to monitor the quality of the food. You should definitely choose fresh and less processed foods and follow the correct cooking methods. In addition to nutrition, physical activity and adequate sleep are also an important part of a healthy lifestyle.
Unfortunately, various studies show that a very large proportion of people do not eat a healthy and balanced diet.
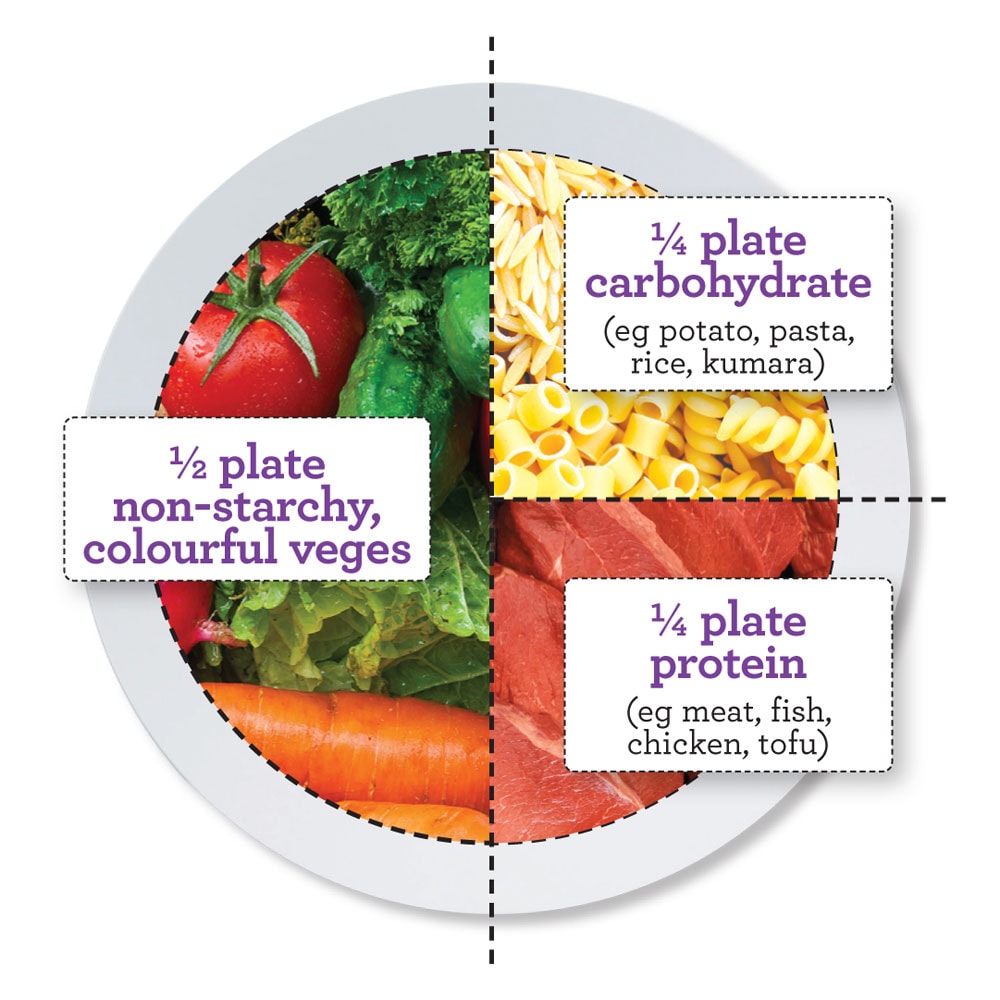
What should you eat more of?
The majority of people still choose white, refined flour products such as pasta, bread, cakes, etc. from store shelves. White rice also often finds its way to people’s meals. Be it Basmati, Long Grain, Jasmine or Porridge Rice. Whole grain products should be chosen instead of such products. Whole grain flour, -pasta, -porridge, -bread and -rice. For example, raw buckwheat and flours made from it are also very welcome. I make it a point to read the package label in the store. There are many products of which packaging misleads the customer and promises to be whole grain bread or similar, but most of them still contain wheat flour. Rather, choose products that do not contain wheat flour and, if at all, in a small amount.
As a rule, there are also not enough vegetables on people’s diets. Estonian national nutrition and exercise recommendations recommend eating up to 7 portions of vegetables per day. This is about 700 g of vegetables. The menu should include vegetables of as many different colors as possible, and you should definitely not forget legumes. Beans, peas, chickpeas and lentils should appear on the menu every day. Fruits and berries should also be consumed daily. It is nice to be able to consume seasonal fruits and berries. However, you should not overdo it with fruits and berries, because they contain fruit sugar, or fructose, and it is recommended to consume them up to 3 portions a day (300 g) together with nuts and seeds. Nuts and seeds contain fats that are good for our body, and by consuming them together with fruits rich in fructose, they prevent our blood sugar from rising too quickly. Blood sugar remains stable and this in turn prevents snacking and overeating.
You should also eat more fish. According to recommendations, fish should be eaten three times a week, but unfortunately this is not often done. The reason for very frequent under-consumption is the price of fish. Here I emphasize that the more variety of fish we eat, the better. We don’t have to eat salmon three times a week, but it is also very good to eat herring, splinter, sprats, etc.
What should be eaten less?
Our cold counters have a very large selection of different dairy products and they are added every year. Most of these dairy products with attractive and eye-catching packaging should be left in the store. Sweetened yogurts, curd creams and puddings contain a lot of sugar and are not good for our health. From dairy products, preference should be given to unsweetened, unflavored and acidified products. Such dairy products can be flavored at home with berries, sugar-free cocoa, fruits, nuts and seeds.
Various semi-fabricated products should also be avoided. Various pre-prepared foods, sausages, wieners, meatballs, pizzas, frozen fries, etc. Such products contain a lot of saturated fat and salt and, as a rule, very little real food. You could definitely leave a variety of salty and sweet snacks in the store, such as seasoned garlic bread, potato chips, popcorn , cookies, pretzels, etc.
Another big stumbling block is various sweetened beverages. Shop counters have a very large selection of different soft drinks. Both carbonated and non-carbonated. Still something for everyone. The sugar content of such drinks is so high that if you drink one 0.5L soft drink, you could eat one wholesome snack instead. The best thirst quencher is water.
If it all seems difficult for you and you need help, the services include a visit to the store with a nutritional therapist. Let’s go to the store together and check out your favorite products. If necessary, we will choose healthier alternatives together.
What is nutritional counselling?
Nutrition counselling is based on promoting nutrition, achieving a healthy weight, and providing nutritional counselling to healthy people.
You could consider nutritional counselling if you want to improve your eating habits, achieve weight goals, or simply gain knowledge about healthy eating. A nutritionist will assist you with personally tailored advice that will help you eat healthily and in a balanced way. Nutrition counselling is an investment in your health and well-being and helps you make lasting changes in your eating habits.
Choose nutrition counselling if you want general instructions and recommendations regarding a healthy diet and lifestyle, and you do not have specific health problems that require a more specific approach. A nutritionist can be of great help, for example, when it comes to losing weight (or gaining weight) in a way that is healthy and creates lasting results.
What is nutritional therapy?
Nutritional therapy is an evidence-based approach to human health. A balanced and healthy diet helps to improve the quality of life and ensures good health.
What is the difference between nutrition counselling and nutrition therapy?
The roles of a nutritional therapist and nutritionist may seem similar, but there are major differences. Both specialists are engaged in nutritional counseling, but their educational background and competencies are different.
A nutritional therapist is a highly educated professional who has a deeper understanding of the relationship between nutrition and the physiology of the body and uses this knowledge to prevent, alleviate and support the treatment of various health problems and diseases. Nutritional therapists can work in healthcare facilities, hospitals, clinics and as independent practitioners.
A graduate of the nutrition therapist level offers nutrition therapy to patients with the following disease groups: cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, anemia, kidney disease, osteoporosis, allergies, cancer, podagra, reflux disease (GERD), irritable bowel syndrome, celiac disease, nutritional problems after bariatric surgery.
The focus of nutritionists is generally on promoting healthy eating, achieving a healthy weight, and providing nutritional counseling to healthy people.
Choose nutrition counselling if you want general instructions and recommendations regarding a healthy diet and lifestyle, and you do not have specific health problems that require a more specific approach. A nutritionist can be of great help, for example, when it comes to losing weight (or gaining weight) in a way that is healthy and creates lasting results.
Choose nutritional therapy if you have: cardiovascular disease, cancer, diabetes, anaemia, kidney failure, osteoporosis, allergies, podagra, reflux disease, irritable bowel syndrome, celiac disease or have undergone bariatric surgery. You can come to nutritional therapy both during and after the illness.
When would it be wise to come to nutritional therapy?
With a healthy diet, it is possible to prevent various diseases such as cardiovascular diseases, cancer, diabetes, etc. However, with nutritional therapy, it is possible to support the body during and after the illness. Nutritional therapy can help with both simpler (effective and healthy weight loss) and more difficult (blood pressure disease, diabetes, etc.) concerns.
What does a nutrition therapy session consist of?
When registering for an appointment with a nutrition therapist, you must first fill out a questionnaire, based on which the nutrition therapist gets a complete picture of the client’s condition, wishes, and goals, and the questionnaire also helps the therapist prepare for the client meeting . During the therapy, the completed questionnaire is already reviewed together with the client, and the therapist shares tips for correcting the diet and prepares a plan that will help the client on his journey to becoming healthier and supporting his health.
How often would it be wise to go to nutritional therapy?
The frequency of nutritional therapy depends on the client’s individual needs, goals and health status. In some cases, one or two sessions are enough to get an overview of a healthy diet and make the necessary changes. Sometimes it may be necessary to see a nutritional therapist regularly for several months or more. The duration and frequency of nutritional therapy depends on the individual’s development and recovery. It is important to understand that each person’s needs are different and depending on that, a specific plan can be put in place.